本文最后更新于 713 天前,其中的信息可能已经过时,如有错误请发送邮件到wuxianglongblog@163.com
ufunc 对象
Numpy 有两种基本对象:ndarray (N-dimensional array object) 和 ufunc (universal function object)。ndarray 是存储单一数据类型的多维数组,而 ufunc 则是能够对数组进行处理的函数。
例如,我们之前所接触到的二元操作符对应的 Numpy 函数,如 add,就是一种 ufunc 对象,它可以作用于数组的每个元素。
import numpy as npa = np.array([0,1,2])
b = np.array([2,3,4])
np.add(a, b)array([2, 4, 6])查看支持的方法:
dir(np.add)['__call__',
'__class__',
'__delattr__',
'__doc__',
'__format__',
'__getattribute__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__name__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__',
'accumulate',
'at',
'identity',
'nargs',
'nin',
'nout',
'ntypes',
'outer',
'reduce',
'reduceat',
'signature',
'types']除此之外,大部分能够作用于数组的数学函数如三角函数等,都是 ufunc 对象。
特别地,对于二元操作符所对应的 ufunc 对象,支持以下方法:
reduce 方法
op.reduce(a)将op沿着某个轴应用,使得数组 a 的维数降低一维。
add 作用到一维数组上相当于求和:
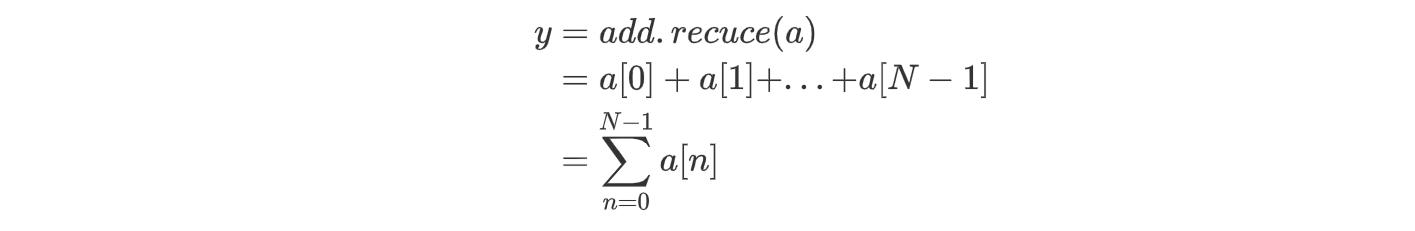
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
np.add.reduce(a)10多维数组默认只按照第一维进行运算:
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
np.add.reduce(a)array([5, 7, 9])指定维度:
np.add.reduce(a, 1)array([ 6, 15])作用于字符串:
a = np.array(['ab', 'cd', 'ef'], np.object)
np.add.reduce(a)'abcdef'逻辑运算:
a = np.array([1,1,0,1])
np.logical_and.reduce(a)Falsenp.logical_or.reduce(a)Trueaccumulate 方法
op.accumulate(a)accumulate 可以看成保存 reduce 每一步的结果所形成的数组。
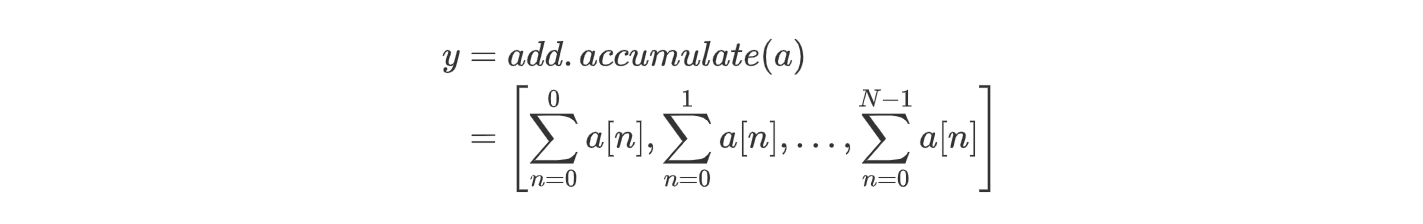
与之前类似:
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
np.add.accumulate(a)array([ 1, 3, 6, 10])a = np.array(['ab', 'cd', 'ef'], np.object)
np.add.accumulate(a)array(['ab', 'abcd', 'abcdef'], dtype=object)a = np.array([1,1,0,1])
np.logical_and.accumulate(a)array([ True, True, False, False], dtype=bool)np.logical_or.accumulate(a)array([ True, True, True, True], dtype=bool)reduceat 方法
op.reduceat(a, indices)reduceat 方法将操作符运用到指定的下标上,返回一个与 indices 大小相同的数组:
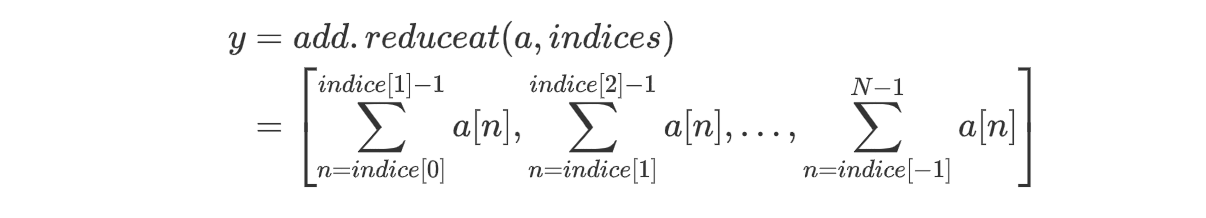
a = np.array([0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
indices = np.array([1,4])
np.add.reduceat(a, indices)array([60, 90])这里,indices 为 [1, 4],所以 60 表示从下标1(包括)加到下标4(不包括)的结果,90 表示从下标4(包括)加到结尾的结果。
outer 方法
op.outer(a, b)对于 a 中每个元素,将 op 运用到它和 b 的每一个元素上所得到的结果:
a = np.array([0,1])
b = np.array([1,2,3])
np.add.outer(a, b)array([[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4]])注意有顺序的区别:
np.add.outer(b, a)array([[1, 2],
[2, 3],
[3, 4]])