本文最后更新于 704 天前,其中的信息可能已经过时,如有错误请发送邮件到wuxianglongblog@163.com
Theano 条件语句
theano 中提供了两种条件语句,ifelse 和 switch,两者都是用于在符号变量上使用条件语句:
ifelse(condition, var1, var2)- 如果
condition为true,返回var1,否则返回var2
- 如果
switch(tensor, var1, var2)- Elementwise
ifelse操作,更一般化
- Elementwise
switch会计算两个输出,而ifelse只会根据给定的条件,计算相应的输出。
ifelse 需要从 theano.ifelse 中导入,而 switch 在 theano.tensor 模块中。
import theano, time
import theano.tensor as T
import numpy as np
from theano.ifelse import ifelseUsing gpu device 1: Tesla K10.G2.8GB (CNMeM is disabled)假设我们有两个标量参数:$a, b$,和两个矩阵 $\mathbf{x, y}$,定义函数为:
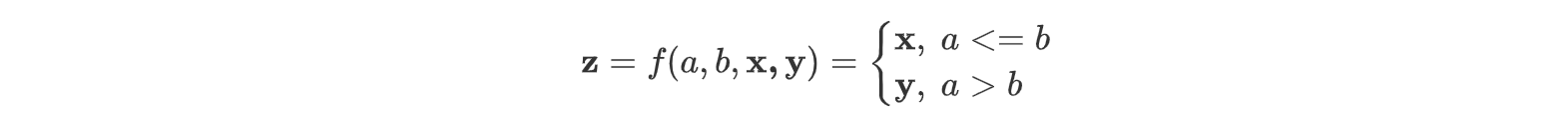
定义变量:
a, b = T.scalars('a', 'b')
x, y = T.matrices('x', 'y')用 ifelse 构造,小于等于用 T.lt(),大于等于用 T.gt():
z_ifelse = ifelse(T.lt(a, b), x, y)
f_ifelse = theano.function([a, b, x, y], z_ifelse)用 switch 构造:
z_switch = T.switch(T.lt(a, b), x, y)
f_switch = theano.function([a, b, x, y], z_switch)测试数据:
val1 = 0.
val2 = 1.
big_mat1 = np.ones((10000, 1000), dtype=theano.config.floatX)
big_mat2 = np.ones((10000, 1000), dtype=theano.config.floatX)比较两者的运行速度:
n_times = 10
tic = time.clock()
for i in xrange(n_times):
f_switch(val1, val2, big_mat1, big_mat2)
print 'time spent evaluating both values %f sec' % (time.clock() - tic)
tic = time.clock()
for i in xrange(n_times):
f_ifelse(val1, val2, big_mat1, big_mat2)
print 'time spent evaluating one value %f sec' % (time.clock() - tic)time spent evaluating both values 0.638598 sec
time spent evaluating one value 0.461249 sec