本文最后更新于 704 天前,其中的信息可能已经过时,如有错误请发送邮件到wuxianglongblog@163.com
森林火灾模拟
之前我们已经构建好了一些基础,但是还没有开始对火灾进行模拟。
随机生长
- 在原来的基础上,我们要先让树生长,即定义
grow_trees()方法 - 定义方法之前,我们要先指定两个属性:
- 每个位置随机生长出树木的概率
- 每个位置随机被闪电击中的概率
- 为了方便,我们定义一个辅助函数来生成随机
bool矩阵,大小与森林大小一致 - 按照给定的生长概率生成生长的位置,将
trees中相应位置设为True
import numpy as np
class Forest(object):
""" Forest can grow trees which eventually die."""
def __init__(self, size=(150,150), p_sapling=0.0025, p_lightning=5.0e-6):
self.size = size
self.trees = np.zeros(self.size, dtype=bool)
self.fires = np.zeros((self.size), dtype=bool)
self.p_sapling = p_sapling
self.p_lightning = p_lightning
def __repr__(self):
my_repr = "{}(size={})".format(self.__class__.__name__, self.size)
return my_repr
def __str__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__
@property
def num_cells(self):
"""Number of cells available for growing trees"""
return np.prod(self.size)
@property
def tree_fraction(self):
"""
Fraction of trees
"""
num_trees = self.trees.sum()
return float(num_trees) / self.num_cells
@property
def fire_fraction(self):
"""
Fraction of fires
"""
num_fires = self.fires.sum()
return float(num_fires) / self.num_cells
def _rand_bool(self, p):
"""
Random boolean distributed according to p, less than p will be True
"""
return np.random.uniform(size=self.trees.shape) < p
def grow_trees(self):
"""
Growing trees.
"""
growth_sites = self._rand_bool(self.p_sapling)
self.trees[growth_sites] = True测试:
forest = Forest()
print forest.tree_fraction
forest.grow_trees()
print forest.tree_fraction0.0
0.00293333333333火灾模拟
- 定义
start_fires():- 按照给定的概率生成被闪电击中的位置
- 如果闪电击中的位置有树,那么将其设为着火点
- 定义
burn_trees():- 如果一棵树的上下左右有火,那么这棵树也会着火
- 定义
advance_one_step():- 进行一次生长,起火,燃烧
import numpy as np
class Forest(object):
""" Forest can grow trees which eventually die."""
def __init__(self, size=(150,150), p_sapling=0.0025, p_lightning=5.0e-6):
self.size = size
self.trees = np.zeros(self.size, dtype=bool)
self.fires = np.zeros((self.size), dtype=bool)
self.p_sapling = p_sapling
self.p_lightning = p_lightning
def __repr__(self):
my_repr = "{}(size={})".format(self.__class__.__name__, self.size)
return my_repr
def __str__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__
@property
def num_cells(self):
"""Number of cells available for growing trees"""
return np.prod(self.size)
@property
def tree_fraction(self):
"""
Fraction of trees
"""
num_trees = self.trees.sum()
return float(num_trees) / self.num_cells
@property
def fire_fraction(self):
"""
Fraction of fires
"""
num_fires = self.fires.sum()
return float(num_fires) / self.num_cells
def _rand_bool(self, p):
"""
Random boolean distributed according to p, less than p will be True
"""
return np.random.uniform(size=self.trees.shape) < p
def grow_trees(self):
"""
Growing trees.
"""
growth_sites = self._rand_bool(self.p_sapling)
self.trees[growth_sites] = True
def start_fires(self):
"""
Start of fire.
"""
lightning_strikes = (self._rand_bool(self.p_lightning) &
self.trees)
self.fires[lightning_strikes] = True
def burn_trees(self):
"""
Burn trees.
"""
fires = np.zeros((self.size[0] + 2, self.size[1] + 2), dtype=bool)
fires[1:-1, 1:-1] = self.fires
north = fires[:-2, 1:-1]
south = fires[2:, 1:-1]
east = fires[1:-1, :-2]
west = fires[1:-1, 2:]
new_fires = (north | south | east | west) & self.trees
self.trees[self.fires] = False
self.fires = new_fires
def advance_one_step(self):
"""
Advance one step
"""
self.grow_trees()
self.start_fires()
self.burn_trees()forest = Forest()
for i in range(100):
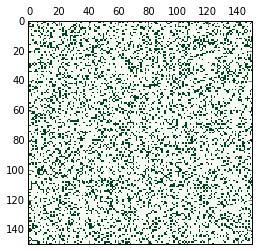
forest.advance_one_step()使用 matshow() 显示树木图像:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
%matplotlib inline
plt.matshow(forest.trees, cmap=cm.Greens)
plt.show()
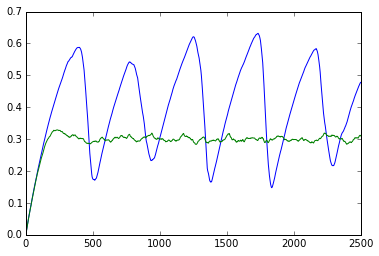
查看不同着火概率下的森林覆盖率趋势变化:
forest = Forest()
forest2 = Forest(p_lightning=5e-4)
tree_fractions = []
for i in range(2500):
forest.advance_one_step()
forest2.advance_one_step()
tree_fractions.append((forest.tree_fraction, forest2.tree_fraction))
plt.plot(tree_fractions)
plt.show()